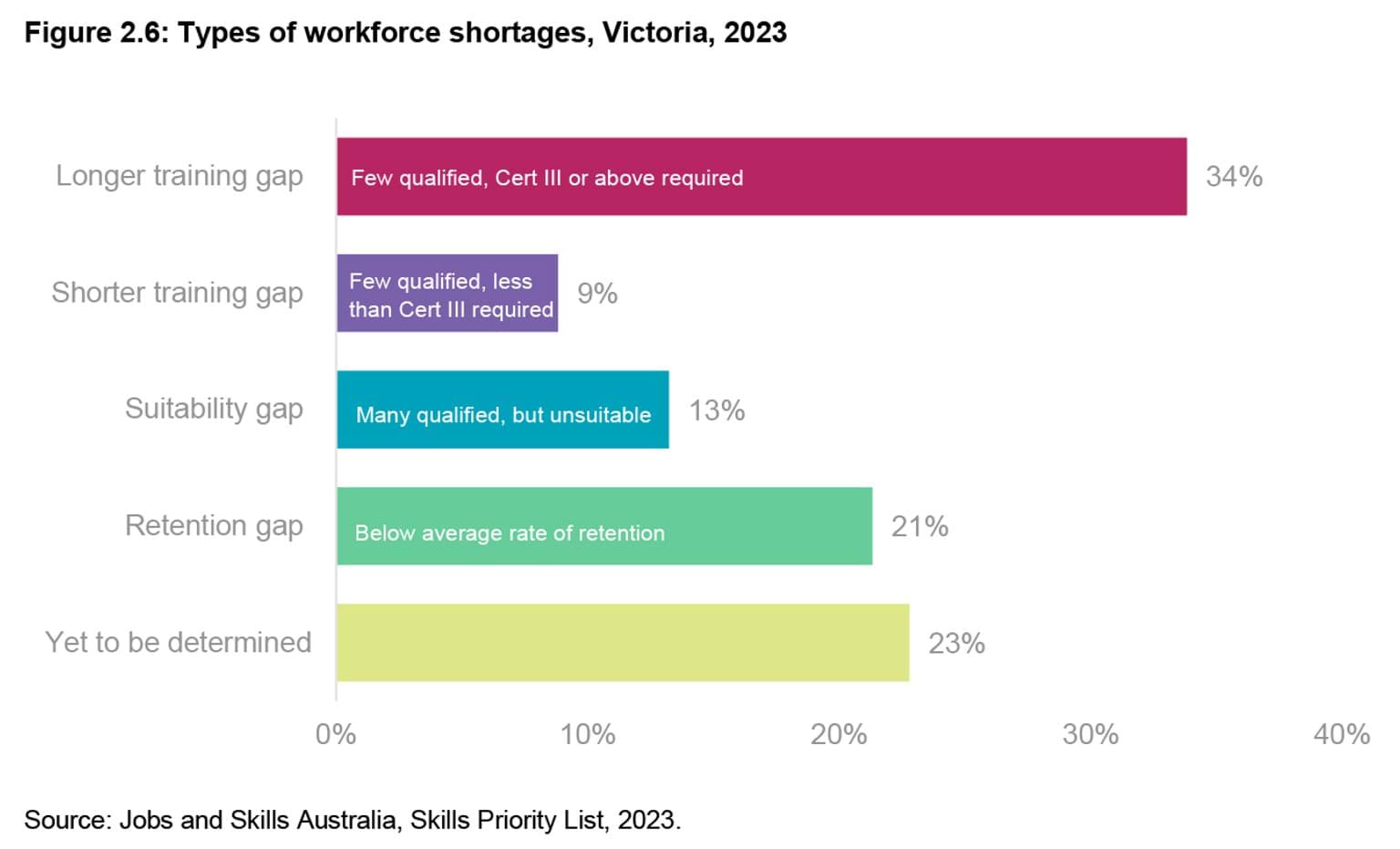
Jobs and Skills Australia has developed a workforce shortage typology that classifies workforce shortages into four types, based on the primary driver of shortage.5
- Longer training gap – few qualified applicants per vacancy and a long training pathway (Certificate III or above).
- Shorter training gap – few applicants per vacancy and qualifications less than Certificate III are required.
- Suitability gap – enough qualified applicants, but they are not regarded as suitable, due to factors such as a lack of employability skills, work experience and/or bias of employers.
- Retention gap – below average rates of retention, potentially reinforced by low numbers of applicants per vacancy.
In Victoria, the most common workforce shortage driver is a longer training gap, followed by a retention gap.
The top 10 occupations with the highest number of internet vacancies are also mostly in shortage. Many of these shortages are driven by a retention gap, but the other drivers of shortages (that is, long training gap, short training gap, and suitability gap) also play a role.
Table 2.2: Occupations with the highest number of internet vacancies in Victoria, June 2024
| Internet vacancies | Workforce shortage driver | |
|---|---|---|
| General clerks | 2,747 | No shortage |
| Sales assistants (general) | 2,367 | N/A |
| Registered nurses | 2,128 | Long training gap |
| Advertising and sales managers | 1,490 | Suitability gap |
| Retail managers | 1,077 | Short training gap |
| Waiters | 1,053 | Retention gap |
| Ageing and disability carers | 1,037 | Retention gap |
| Software and applications programmers | 1,020 | Suitability gap |
| Child carers/early childhood educators | 1,008 | Retention gap |
| Accountants | 995 | No shortage |
Source: Jobs and Skills Australia, Internet Vacancy Index, Internet Vacancies, ANZSCO4 Occupations, States and Territories – June 2024; Jobs and Skills Australia, Skills Priority List, 2023.
Updated